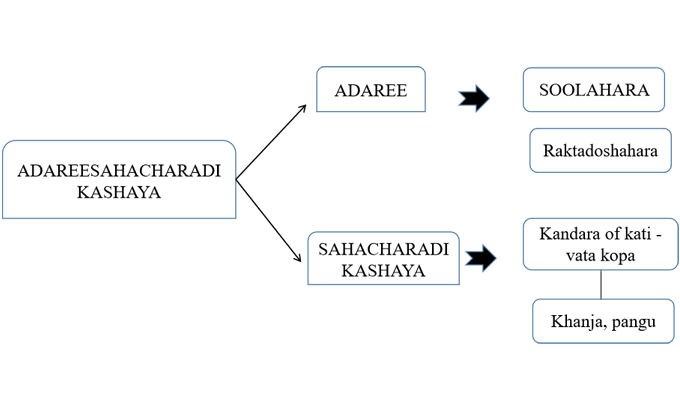
Aadareesahacharadi kashayam is formulated by the addition of Aadaree an indigenous plant, in popular Sahacharadi kashayam (A H) to explore the potential in gait disorder. Addition of Aadaree to the yoga brings its site of action to rakta and mamsa dhatu too as it is vranaropana. The yoga contain total 4 ingredients, they are Aadaree (Caesalpinia mimosoides), Sahachara (Strobilanthes ciliatus), Devadaru (Cedrus deodara), and Nagara (Zingiber officinale).
General indication:Khanja, pangu, adhakaya vata hara.
Ashtavaidya practices:Gridrasi, kateegraha, siragrandhi, khalli and vata khanja.
Experiential Wisdom:
15 ml Kashayam with 60 ml lukewarmwater twice daily before food.
Ketakimooladi thailam /Sahacharadi thailam /Dhanwantharam thailam /Bala thailam.
Tridoshahara, deepana, sulaghna
The cumulative pharmacological property reveals the yoga with tikta-kashaya rasa, laghu-snigdha guna, ushna veerya and katu vipaka. Pharmacological properties contributes tridoshahara, deepana, and sulaghna effects in the management of khanja, pangu, vatakandaka, gridrasi, siragranthi, and mainly adhakayavataroga. Aadareesahacharadi kashayam is effectively practised in pain predominant pathologies affecting the lower limb. Addition of Aadaree brings more soolahara potential to the drug. Khanja and pangu are main indications of the yoga. Both are gait abnormalities due to vata kopa in kati. Aadaree along with sahacharadi kashaya dravya provide more vataharatva to the combination. Aadaree is a seetha veerya drug with pitta-rakta samaka action, thus can be given in acute inflammation affecting sira and kandara which are the upadhatus of rakta. So Aadaree also helps to rectify the pathology of khanja and pangu in which kandara is affected. The ingredients in this formulation such as Strobilanthes ciliatus, Cedrus deodara and Zingiber officinale reported to have anti inflammatory activity. The antioxidant property of Cedrus deodara is attributed to flavonoids, tannins and phenolic compounds and also due to the presence of phenolic compounds in Zingiber officinale. The spasmolytic and analgesic effect was reported due to Sesquiterpenoids in Cedrus deodara and 6-gingerol,8-gingerol, 10-gingerol and 6-shogaol in Zingiber officinale respectively.

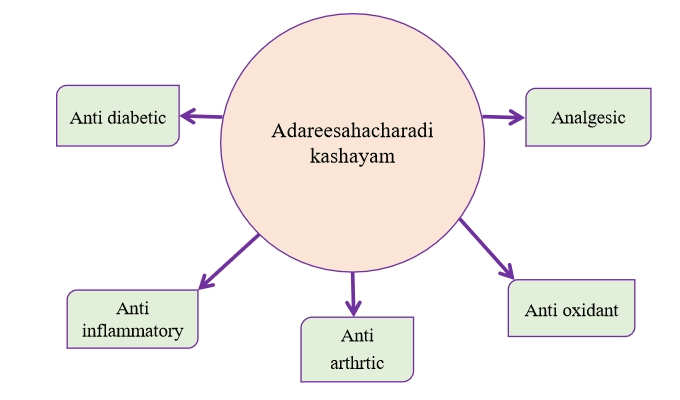
Pharmacological:
Clinical: